Structures |
Structures are encoded as a sequence of fields in the order that they appear in the definition. The encoding for each field is determined by the data type for the field.
All fields specified in the complex type shall be encoded.
Structures do not have a Null value. If an encoder is written in a programming language that allows structures to have null values then the encoder shall create a new instance with default values for all fields and serialize that. Encoders shall not generate an encoding error in this situation.
The following is an example of a structure using C++ syntax:
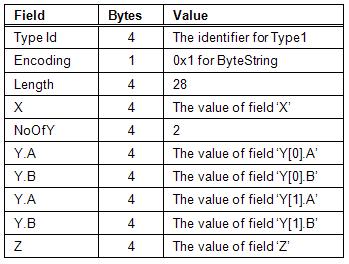
class Type2 { int A; int B; }; class Type1 { int X; int NoOfY; Type2* Y; int Z; };
The Y field is a pointer to an array with a length stored in NoOfY.
An instance of Type1 which contains an array of two Type2 instances would be encoded as 37 byte sequence. If the instance of Type1 was encoded in an ExtensionObject it would have the encoded form shown in Figure 1. The TypeId, Encoding and the Length are fields defined by the ExtensionObject. The encoding of the Type2 instances do not include any type identifier because it is explicitly defined in Type1.