Object |
Objects are used to represent systems, system components, real-world objects and software objects.
The primary objective of the OPC Unified Architecture Address Space is to provide a standard way for servers to represent Objects to clients. The OPC Unified Architecture Object Model has been designed to meet this objective. It defines Objects in terms of Variables and Methods. It also allows relationships to other Objects to be expressed. Figure 1 illustrates the model.
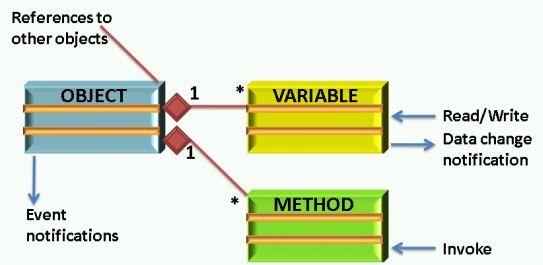
Objects and their components are represented in the Address Space as a set of Nodes described by Attributes and interconnected by References.
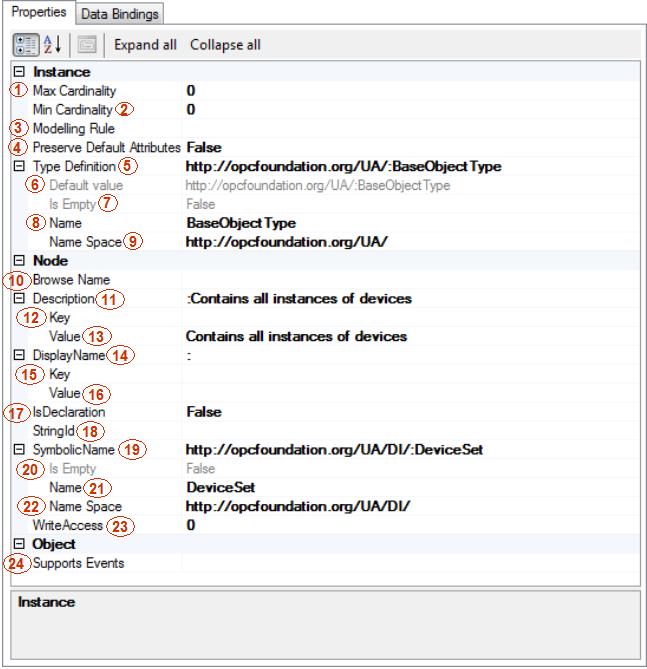
Object properties:
Max Cardinality - this attribute indicates the maximum number of possibly existing instances of this element.
Min Cardinality - this attribute indicates the minimum number of possibly existing instances of this element. If the element has minimal cardinality greater than 0, it is possible to check that it exists in the instantiated nodes.
Modeling Rule - dependent on the value of these properties specified for the components of a type they are used to create appropriate instances while the parent type is instantiated in the address space. The default value is Mandatory. In this case the component is always created with the values of the attributes derived from the inheritance chain. If the value is None it indicates that this node only belongs to the type and is not used to create an instance while the parent type is instantiated. If the node is not a type component the value of this property is ignored.
Preserve Default Attributes - a value indicating whether to preserve default attributes.
Type Definition - the type of this instance pointed out by the HasTypeDefinition reference.
Default value – the default value of the Type Definition.
Is Empty - indicates if the Type Definition is empty.
Name – the name of the TypeDefinition.
Namespace – a namespace that qualifies the name of the TypeDefinition.
Browse Name - a name used in the information model. The validator will create the BrowseName automatically from the SymbolicName. The BrowseName is qualified by the namespace used for the SymbolicName.
Description - optionally a vendor specific description is provided. The validator automatically creates a generic Description from the BrowseName and NodeClass.
Key – an optional key that can be used to look up the Description for other locales in a resource DB.
Value – the value of the Description attribute for the Node.
Display Name – a human readable name for the Node. The validator automatically creates the DisplayName from the BrowseName.
Key – an optional key that can be used to look up the display name for other locales in a resource DB.
Value – the value of the Display Name.
IsDeclaration - this flag indicates that the Node is defined elsewhere and no code will be generated. Nodes that are declarations do not need to be completely defined. They only need to have the information required to generate code for nodes that reference it (e.g. the BaseType).
StringId - an alternate unique identifier for the node. It is used instead of the NumericId if it is specified in the CSV input file.
Symbolic Name - identifies the Node within the ModelDesign or within the containing Node. The SymbolicName should always be specified. It is used to create the BrowseName and SymbolicId if they are not specified.
Is Empty - indicates whether the Symbolic Name is empty.
Name – a name, which is a part of the Symbolic Name.
Namespace – a namespace which qualifies the Name from the Symbolic Name.
Write access - a bit mask that indicates, which attributes are writeable. Optionally the WriteMask Attribute can be provided. If the WriteMask Attribute is provided, it shall set all Attributes to not writeable that are not said to be vendor-specific. For example, the Description Attribute may be set to writeable since a Server may provide a server-specific description for the Node. The NodeId shall not be writeable, because it is defined for each Node in specification.
Supports events - a value indicating whether the Object class node supports events.