CommServer |
Welcome to CommServer
This manual is designed for those using CommServer for the first time. Familiarity with the Windows environment, engineering terminology, Remote Terminal Units, Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition systems is essential.
CommServer is a fully configurable communication server providing OPC connectivity. It provides a multi-protocol, multi-medium and multi-channel redundant access to digital plant-floor devices. To ensure short response time and effective utilization of the physical device communication channels throughput, unique adaptive transfer control and adaptive sampling algorithms are implemented.
CommServer offers the possibility of using many vendor specific communication protocols simultaneously, parallel handling of independent communication channels and redundant links with remote physical devices. Any user can define logical sets of devices (segments) with common address or scanning rules (e.g. connected by one ISDN modem or satellite transceiver). New protocols (data providers) can easily be added by plug-ins. It provides the possibility of using various communication media simultaneously, including copper and fiber optic networks, digital radio, ISDN, GSM-GPRS, WIFI and satellite transponders. The physical data communication network is monitored and the acquired diagnostic data are provided as OPC tags.
CommServer offers unique algorithms of scheduling the process responsible for updating of the device data cache, based on original solutions in the field of multithreaded technology. These algorithms utilize dynamic priorities and adaptable scanning rules defined for physical process variables grouped into sets to optimize the communication throughput. The scanning priority of the group and, as a consequence, the device sampling rate is a function of:
the process control state represented by selected alarm tags and
throughput of the medium used.
CommServer is fully configurable by an included configuration application (NetworkConfig). The configuration is stored in a widely accepted XML format, so it can easily be managed by a foreign application (all protocol parameters, interfaces, segments, channels, tags and tag groups are defined in the configuration file). The tags can be imported and exported from SQL database e.g. ORACLE - a dictionary or SCADA system e.g. WIZCON configuration files. It allows a smooth migration and integration process with third party SCADA software.
An example of a system running CommServer is shown in the picture below:
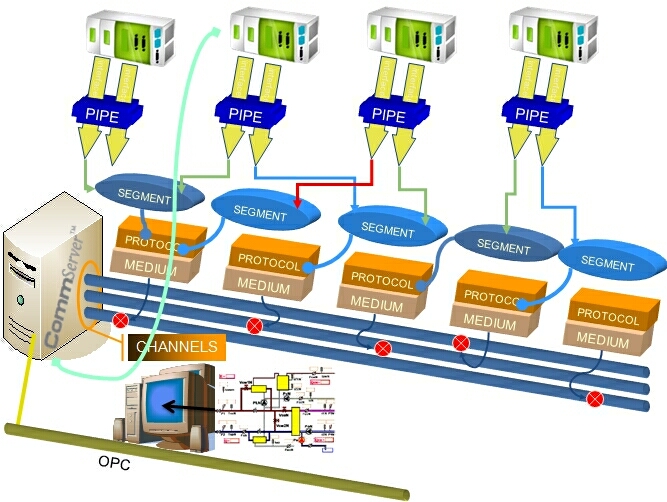
Explanation of the system components:
Base Station – computer hosting CommServer software – it is responsible for redundant communication with plant-floor devices;
Channel – virtual communication object that models independent communication via various types of media (radio, GSM-GPRS, cable TV, satellite, FO, etc…). Communication through different channels is conducted simultaneously.
Data Provider = medium + protocol or simulator – it is responsible for providing data to the communication server. It can play many roles including: communication with remote plant-floor devices, simulation of a process or monitoring of the local OS or local network performance counters, cache providing horizontal communication. To establish communication with a remote unit, many components implementing a couple of protocol / communication medium are available.
Segment – communication segment is a virtual group of plant-floor devices that have the same address (IP, dial number, etc.) and needs to be served using common connection (the same communication path). The basic scanning rule for the segment is that only one segment per channel is active at any instant to provide mutually exclusive access to common resources or communication medium. The segment is also responsible for connection management of the connation oriented transport protocols, e.g. TCP, ISDN, etc.
The segment can be in one of the following states:
Establishing connection;
Transmitting;
Closing connection;
Inactive;
Port - plant-floor devices physical (independently addressed on the segment sub-network) communication interface; e.g. serial port of a PLC connected to RS485 field bus.
Pipe - a couple of selected ports representing single bidirectional data stream. The main rule for a pipe is that only one port belonging to the pipe is active at the same time. To provide redundancy after failure of one communication path, another port belonging to the same pipe is activated immediately to establish a new communication path. Behind the scene, availability of non-active ports is checked periodically.
CommServer requires the following hardware and software to run:
Operating System: Windows NT 4.0 Sp 6.0a, Windows 2000, Windows XP;
Additional software: .NET Framework 2.0, Internet Explorer, OPC Core Components 2.00 Redistributable 2.30+
Additional hardware: Standard Serial Ports (COM), Ethernet Card. Hardware depends on system requirements.